ISS Light Sources

- Stock: Contact us for details
- Click here to: Contact us
- Model: Light Sources
ISS Light Sources
Laser Diodes

The laser diodes, packaged into a compact housing, are powered by a ±15 V supply. The focal lens can be adjusted over the range 15 cm – 200 cm. Modulation up to 400 MHz can be attained by using an external frequency generator. Digital modulation (TTL) is attainable up to 80 MHz.
Compatible with Q2, PL1, ChronosBH, ChronosDFD, and PC1.
| Part No. | Emission Wavelength (nm) | Average power at 10 MHz modulation (mW) |
| N322 | 375 ± 5 | 0.97 |
| N325 | 405 ± 5 | 6.90 |
| N328 | 445 ± 5 | 6.70 |
| N332 | 473 ± 5 | 4.63 |
| N334 | 488 ± 5 | 5.00 |
| N339 | 514 ± 5 | 2.24 |
| N352 | 635 ± 5 | 4.47 |
| N354 | 660 ± 5 | 4.15 |
| N356 | 690 ± 5 | 4.85 |
| N358 | 780 ± 5 | 4.95 |
| N360 | 808 ± 5 | 2.55 |
| N362 | 830 ± 5 | 6.50 |
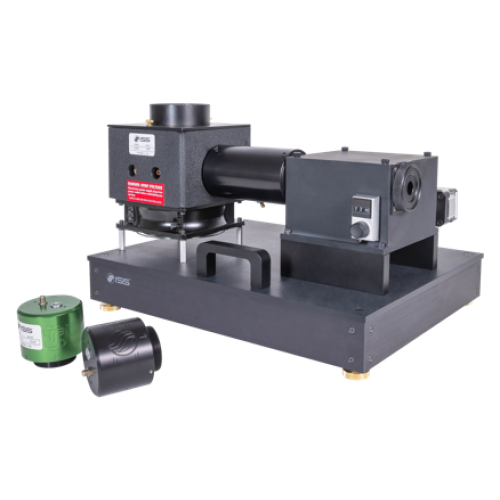
Illuminator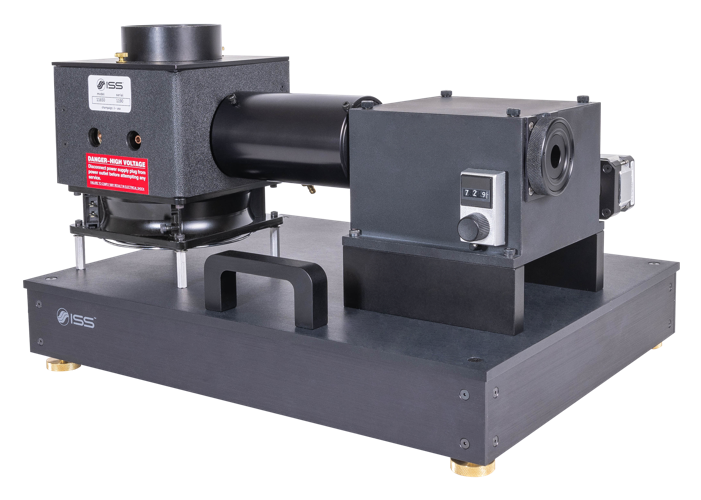
The illuminator is a convenient source of radiation in the wavelength range from 230 nm to 850 nm. The light is generated by a xenon arc lamp and the wavelength is selected by a single-grating monochromator with a grating blazed in the UV. At the exit of the monochromator the light is collected by a 180 mm-long fiber bundle covering the rectangular shape of the slit to maximize the light collection. The delivery end features a round aperture; a telescopic lens is positioned at the exit of the fiber for allowing the control of the parallelism and size of the illumination beam.
The components are conveniently mounted on a baseplate for easy positioning and transportation in the laboratory space. The wavelength is selected by manually moving the rotating dial on the monochromator.
Alternatively, the monochromator can be controlled through the computer by using a Motor Controller unit and the Vinci software; the wavelength can then be selected through the computer.
| File Name | Size | Link |
|---|---|---|
|
|
207.42KiB | Download |